Is your business ready to meet the global regulations on data privacy? With data compliance becoming increasingly complex, especially across borders, understanding the GDPR Vs CCPA debate is essential.
These two major privacy laws shape how businesses collect, manage, and protect personal data, but how do they truly compare, and what sets them apart?
This blog will explore the key similarities and differences between GDPR and CCPA, provide a structured comparison, and offer compliance guidance that businesses can apply across both jurisdictions.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enforced since May 2018, is Europe’s primary data protection law. It governs how businesses process the personal data of individuals within the European Union. It applies globally to any organisation interacting with EU citizens, regardless of location.
Key principles of GDPR include:
This regulation demands businesses follow strict GDPR Vs CCPA standards, including having a lawful basis for processing and implementing strong technical controls.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which came into effect on January 1, 2020, focuses on consumer privacy rights for California residents. It mandates disclosures about data usage and allows consumers to access, delete, or opt out of the sale of their personal information. It requires businesses to inform consumers how they use their data and grants consumers the right to request, modify, or refuse the ability to sell their data.
The law applies to for-profit businesses meeting certain criteria, such as:
Understanding how the CCPA Vs GDPR compliance structure works is essential for organisations simultaneously handling U.S. and EU data.
Despite originating from different regions, GDPR and CCPA share several common goals in data privacy protection.
Both regulations ensure individuals can access personal data held by companies. This empowers users to verify data accuracy and understand how their data is being used.
Businesses must inform consumers what data is being collected and for what purpose. Clear, accessible privacy notices are a core requirement under both laws.
Under GDPR and CCPA, consumers have the right to request deletion of their personal data. While GDPR’s right to erasure is broader, both laws recognise this fundamental privacy right.
Each regulation emphasises implementing robust data protection mechanisms throughout the entire data lifecycle. Proactive data minimisation, access control, and secure storage are common expectations.
While both GDPR and CCPA aim to protect personal data, they differ in legal structure, enforcement, and operational scope. Below is a deeper look at the differences between CCPA and GDPR that every organisation should understand.
GDPR applies to any organisation, inside or outside the EU, that processes personal data of EU residents. It enforces global accountability, making location irrelevant if EU data is involved.
CCPA applies only to businesses operating in California or dealing with California residents, provided they meet certain thresholds. This makes it more localised, but still impactful for national and international companies.
GDPR uses a broad definition, including data like names, identification numbers, location data, and biometric information. It also includes special categories like health and political opinions, enhancing the law’s depth.
CCPA, on the other hand, defines personal information as anything that identifies, relates to, or could be linked to a consumer or household. It emphasises identifiable data like IP addresses, purchase history, or device IDs, as noted in the CCPA vs GDPR data guidance.
GDPR requires a lawful basis for data processing, such as consent, contract necessity, or legal obligations. Businesses must document their legal basis and demonstrate compliance when challenged.
CCPA does not outline lawful bases for data processing. Instead, it focuses on consumer rights, allowing them to know, delete, or opt out of the sale of their data. This distinction is central in discussions on CCPA compliance vs GDPR strategy.
GDPR mandates clear, affirmative, informed consent before collecting or processing personal data. Pre-ticked boxes or passive acceptance do not qualify as valid consent under the law.
CCPA does not require prior consent in most cases but insists that consumers be given the right to opt out of data sales. Businesses must include a “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link, a fundamental aspect of GDPR vs CCPA requirements.
GDPR penalties are among the strictest globally, with fines of up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual turnover, whichever is higher. These are enforced by independent data protection authorities.
CCPA fines are capped at $7,500 for intentional violations and $2,500 for unintentional ones. While less severe, CCPA fines vs GDPR still pose a considerable risk for non-compliant businesses.
GDPR demands strong accountability, requiring businesses to implement measures such as encryption, pseudonymisation, and data protection impact assessments (DPIAs). Organisations must prove their systems are secure by design.
CCPA expects businesses to use “reasonable security procedures and practices,” but lacks specificity. This flexibility can be challenging, especially when aligning with CCPA vs GDPR standards.
GDPR provides the right to data portability, allowing users to transfer their data to another service provider. It also restricts automated decision-making and profiling without user consent.
CCPA allows consumers to access their data, but does not grant full portability rights. It also lacks explicit controls over profiling, further differentiating the GDPR vs CCPA chart.
GDPR requires businesses to report personal data breaches to supervisory authorities within 72 hours. If the breach is high risk, the individuals involved must also be informed.
CCPA requires prompt notification of data breaches, but does not specify an exact timeframe. However, failure to notify consumers on time can lead to legal action.
GDPR mandates appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) under certain conditions, maintaining detailed records of data activities, and conducting DPIAs when necessary. Compliance must be demonstrable at all times.
CCPA requires businesses to update privacy policies regularly, provide a toll-free number or online form for data requests, and respond to consumer rights requests within specific timeframes. These are vital for maintaining a GDPR vs CCPA compliant privacy policy.
GDPR is enforced by independent supervisory authorities in each EU member state. They investigate complaints, issue fines, and ensure consistent regulation application.
CCPA is enforced by the California Attorney General, who oversees compliance, investigates violations, and issues penalties. The law also allows for enforcement through civil actions, ensuring businesses take privacy obligations seriously.
| Feature | GDPR | CCPA |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Scope | Applies globally to any business processing EU data | Applies to California-based or related entities |
| Legal Basis for Processing | Requires consent, legal obligation, or legitimate interest | No explicit legal basis required |
| Consent Requirement | Opt-in consent required before processing | Opt-out option required for data sales |
| Penalties | Up to €20M or 4% global turnover | $2,500 (unintentional), $7,500 (intentional) per violation |
| Enforcement | EU Data Protection Authorities | California Attorney General and private right of action |
| Data Portability | Supported; users can transfer data between services | Not mandated |
| Data Breach Notification | Must notify within 72 hours | Required but no strict timeframe |
| Security Measures | Encryption, DPIAs, privacy by design | Reasonable security practices expected |
| Profiling and Automated Decisions | Restricted unless explicit consent is given | No restrictions on profiling or automated decision-making |
Meeting the obligations of both laws may seem complex, but with structured planning and the right tools, it becomes manageable. Here’s how to align your privacy strategy with GDPR vs CCPA laws effectively:
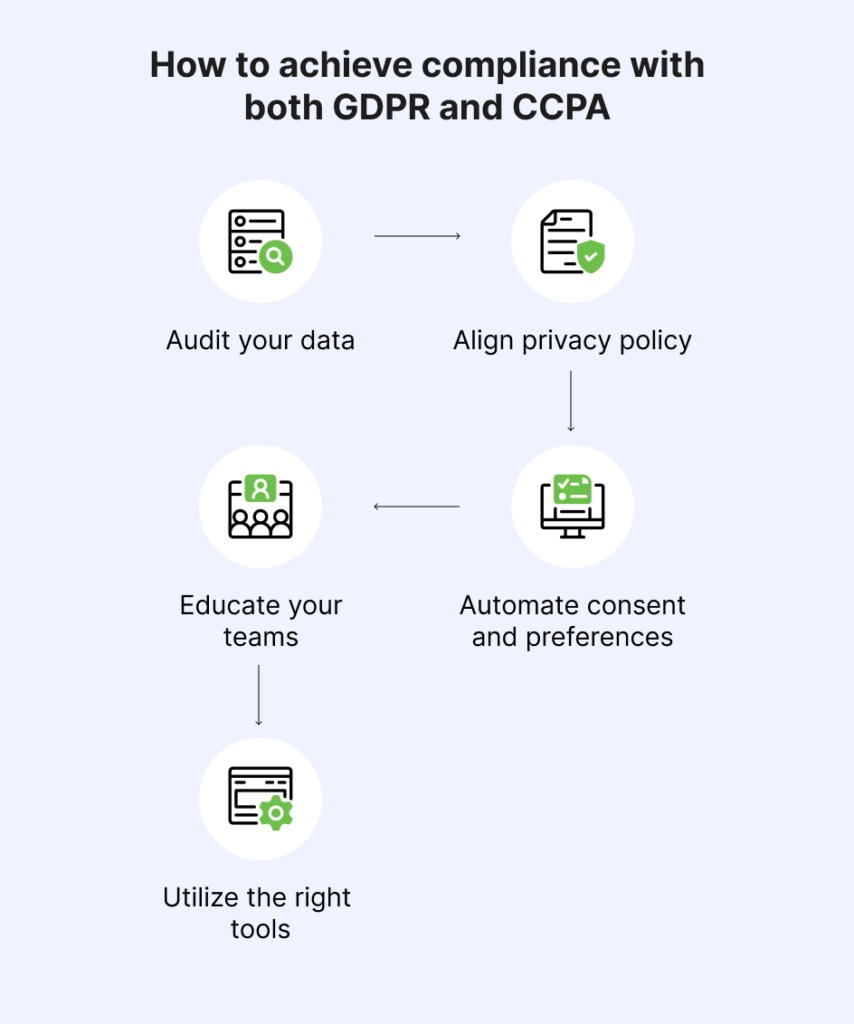
By streamlining these actions, businesses can build robust, scalable processes that minimise risk and align with global privacy expectations.
Navigating CCPA vs GDPR laws is not just about avoiding fines; it’s about building a culture of trust. The differences in enforcement, scope, and terminology require a tailored approach, but the core principle remains the same: protect the individual’s right to data privacy.
Understanding both laws allows you to develop a more resilient, scalable, and compliant privacy program, capable of withstanding global scrutiny and consumer expectations.
Let Seers AI make it simple. Our AI-powered consent management platform removes the confusion around GDPR and CCPA, so you can easily protect your data and build trust with your customers.
Start Free TodayThe most significant difference is how they handle consent. GDPR wants businesses to ask users before collecting data (opt-in), while CCPA allows data collection unless users opt out. On the same note, while GDPR applies to any individual dealing with EU residents’ data ubiquitously, CCPA specifically targets California residents.
However, GDPR has a wider definition regarding details, which can be names, emails, location, and even political affiliations. CCPA pays significant attention to the identifiers such as IP addresses, the history of purchase, and browser history. They offer protection to personal information, but with a slight variation.
Under GDPR, you need clear permission before placing cookies, especially tracking cookies. CCPA doesn’t require prior consent, but users must be able to opt out of the sale of their data. Thus, while GDPR requires steps in advance, CCPA is similar in empowering consumers and providing them with a choice afterwards.
If your business targets both EU citizens and Californian residents, then the answer is yes, it has to adhere to both. Each law has its own rules to follow, and breaking them can lead to legal problems. It’s all about protecting the rights of users in the areas where they live.
Both of these laws give users the right to be informed about what data is collected, access it, delete it, and more. Some other rights that were introduced by GDPR are the right to rectification or to object to how data is processed. CCPA focuses more on transparency and opting out of data sales.

United Kingdom
24 Holborn Viaduct
London, EC1A 2BN
Get our monthly newsletter with insightful blogs and industry news
By clicking “Subcribe” I agree Terms and Conditions

Seers Group © 2026 All Rights Reserved
Terms of use | Privacy policy | Cookie Policy | Sitemap | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information.